I recently announced that I’d accepted a job offer from Automattic and I’ll be starting work there in October. As I first decided to apply for the job 128 days ago – a nice round number – I thought I’d share with you my journey over the last 128 days.
Other people have written at length about their experience of being accepted (sometimes on the second or third attempt) or rejected by Automattic as well as about their interview process and the kind of person who works for them. Or if you prefer, there are more-objective articles about how Automattic’s hiring procedures are unique. My story, though is a work-in-progress: written contemporaneously and still unfolding (see if I’ve written more yet!).
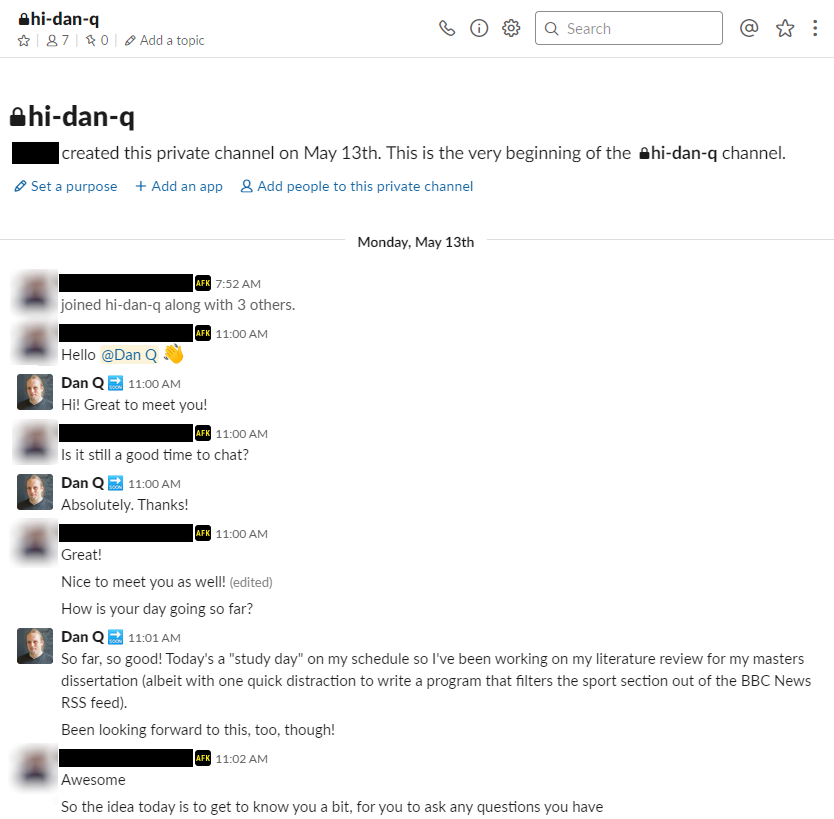
Here’s my timeline so far:
Application (days -179 to -178)
Like many geeks, I keep a list of companies that I’ve fantasised about working for some day: mine includes the Mozilla Foundation and DuckDuckGo, for example, as well as Automattic Inc. In case it’s not obvious, I like companies that I feel make the Web a better place! Just out of interest, I was taking a look at what was going on at each of them. My role at the Bodleian, I realised a while ago, is likely to evolve into something different probably in the second-half of 2020 and I’d decided that when it does, that would probably be the point at which I should start looking for a new challenge. What I’d intended to do on this day 128 days ago, which we’ll call “day -179”, was to flick through the careers pages of these and a few other companies, just to get a better understanding of what kinds of skills they were looking for. I didn’t plan on applying for new jobs yet: that was a task for next-year-Dan.

But then, during a deep-dive into the things that make Automattic unique (now best-explained perhaps by this episode of the Distributed podcast), something clicked for me. I’d loved the creed for as long as I’d known about it, but today was the day that I finally got it, I think. That was it: I’d drunk the Kool-Aid, and it was time to send off an application.
I sat up past midnight on day -179, sending my application by email in the small hours of day -178. In addition to attaching a copy of my CV I wrote a little under 2,000 words about why I think I’m near-uniquely qualified to work for them: my experience of distributed/remote working with SmartData and (especially) Three Rings, my determination to remain a multidisciplinary full-stack developer despite increasing pressure to “pick a side”, my contributions towards (and use, since almost its beginning of) WordPress, and of course the diverse portfolio of projects large and small I’ve worked on over my last couple of decades as a software engineer.

At the time of my application (though no longer, as a result of changes aimed at improving gender equality) the process also insisted that I include a “secret” in my application, which could be obtained by following some instructions and with only a modest understanding of HTTP. It could probably be worked out even by a developer who didn’t, with a little of the kind of research that’s pretty common when you’re working as a coder. This was a nice and simple filtering feature which I imagine helps to reduce the number of spurious applications that must be read: cute, I thought.

I received an automated reply less that a minute later, and an invitation to a Slack-based initial interview about a day and a half after that. That felt like an incredibly-fast turnaround, and I was quite impressed with the responsiveness of what must necessarily be a reasonably-complex filtering and process-management process… or perhaps my idea of what counts as “fast” in HR has been warped by years in a relatively slow-moving and bureaucratic academic environment!
Initial Interview (day -158)
I’ve got experience on both sides of the interview table, and I maintain that there’s no single “right” way to recruit – all approaches suck in different ways – but the approaches used by companies like Automattic (and for example Bytemark, who I’ve shared details of before) at least show a willingness to explore, understand, and adopt a diversity of modern practices. Automattic’s recruitment process for developers is a five-step (or something like that) process, with the first two stages being the application and the initial interview.
My initial interview took place 20 days after my application: entirely over text-based chat on Slack, of course.

The initial interview covered things like:
- Basic/conversational questions: Why I’d applied to Automattic, what interested me about working for them, and my awareness of things that were going on at the company at the moment.
- Working style/soft skills: Questions about handling competing priorities in projects, supporting co-workers, preferred working and development styles, and the like.
- Technical/implementation: How to realise particular ideas, how to go about debugging a specific problem and what the most-likely causes are, understanding clients/audiences, comprehension of different kinds of stacks.
- My questions/lightweight chat: I had the opportunity to ask questions of my own, and a number of mine probed my interviewer as an individual: I felt we’d “clicked” over parts of our experience as developers, and I was keen to chat about some up-and-coming web technologies and compare our experiences of them! The whole interview felt about as casual and friendly as an interview ever does, and my interviewer worked hard to put me at ease.
Skills Test (day -154)
At the end of the interview, I was immediately invited to the next stage: a “skills test”: I’d be given access to a private GitHub repository and a briefing. In my case, I was given a partially-implemented WordPress plugin to work on: I was asked to –
- add a little functionality and unit tests to demonstrate it,
- improve performance of an existing feature,
- perform a security audit on the entire thing,
- answer a technical question about it (this question was the single closest thing to a “classic programmer test question” that I experienced), and
- suggest improvements for the plugin’s underlying architecture.
I was asked to spend no more than six hours on the task, and I opted to schedule this as a block of time on a day -154: a day that I’d have otherwise been doing freelance work. An alternative might have been to eat up a couple of my evenings, and I’m pretty sure my interviewer would have been fine with whatever way I chose to manage my time – after all, a distributed workforce must by necessity be managed firstly by results, not by approach.

My amazingly-friendly “human wrangler” (HR rep), ever-present in my Slack channel and consistently full of encouragement and joy, brought in an additional technical person who reviewed my code and provided feedback. He quite-rightly pulled me up on my coding standards (I hadn’t brushed-up on the code style guide), somewhat-monolithic commits, and a few theoretical error conditions that I hadn’t accounted for, but praised the other parts of my work.
Most-importantly, he stated that he was happy to recommend that I be moved forward to the next stage: phew!
Trial (days -147 through -98)
Of all the things that make Automattic’s hiring process especially unusual and interesting, even among hip Silicon Valley(-ish, can a 100% “distributed” company really be described in terms of its location?) startups, probably the most (in)famous is the trial contract. Starting from day -147, near the end of May, I was hired by Automattic as a contractor, given a project and a 40-hour deadline, at $25 USD per hour within which to (effectively) prove myself.
As awesome as it is to be paid to interview with a company, what’s far more-important is the experience of working this way. Automattic’s an unusual company, using an unusual workforce, in an unusual way: I’ve no doubt that many people simply aren’t a good fit for distributed working; at least not yet. (I’ve all kinds of thoughts about the future of remote and distributed working based on my varied experience with which I’ll bore you another time.) Using an extended trial as an recruitment filter provides a level of transparency that’s seen almost nowhere else. Let’s not forget that an interview is not just about a company finding the right employee for them but about a candidate finding the right company for them, and a large part of that comes down to a workplace culture that’s hard to define; instead, it needs to be experienced.
For all that a traditional bricks-and-mortar employer might balk at the notion of having to pay a prospective candidate up to $1,000 only to then reject them, in addition to normal recruitment costs, that’s a pittance compared to the costs of hiring the wrong candidate! And for a company with an unusual culture, the risks are multiplied: what if you hire somebody who simply can’t hack the distributed lifestyle?

It was close to this point, though, that I realised that I’d made a terrible mistake. With an especially busy period at both the Bodleian and at Three Rings and deadlines looming in my masters degree, as well as an imminent planned anniversary break with Ruth, this was not the time to be taking on an additional piece of contract work! I spoke to my human wrangler and my technical supervisor in the Slack channel dedicated to that purpose and explained that I’d be spreading my up-to-40-hours over a long period, and they were very understanding. In my case, I spent a total of 31½ hours over six-and-a-bit weeks working on a project clearly selected to feel representative of the kinds of technical problems their developers face.
That’s reassuring to me: one of the single biggest arguments against using “trials” as a recruitment strategy is that they discriminate against candidates who, for whatever reason, might be unable to spare the time for such an endeavour, which in turn disproportionately discriminates against candidates with roles caring for other (e.g. with children) or who already work long hours. This is still a problem here, of course, but it is significantly mitigated by Automattic’s willingness to show significant flexibility with their candidates.
I was given wider Slack access, being “let loose” from the confines of my personal/interview channel and exposed to a handful of other communities. I was allowed to mingle amongst not only the other developers on trial (they have their own channel!) but also other full-time staff. This proved useful – early on I had a technical question and (bravely) shouted out on the relevant channel to get some tips! After every meaningful block of work I wrote up my progress via a P2 created for that purpose, and I shared my checkins with my supervisors, cumulating at about the 20-hour mark in a pull request that I felt was not-perfect-but-okay…
…and then watched it get torn to pieces in a code review.
Everything my supervisor said was fair, but firm. The technologies I was working with during my trial were ones on which I was rusty and, moreover, on which I hadn’t enjoyed the benefit of a code review in many, many years. I’ve done a lot of work solo or as the only person in my team with experience of the languages I was working in, and I’d developed a lot of bad habits. I made a second run at the pull request but still got shot down, having failed to cover all the requirements of the project (I’d misunderstood a big one, early on, and hadn’t done a very good job of clarifying) and having used a particularly dirty hack to work-around a unit testing issue (in my defence I knew what I’d done there was bad, and my aim was to seek support about the best place to find documentation that might help me solve it).
I felt deflated, but pressed on. My third attempt at a pull request was “accepted”, but my tech supervisor expressed concerns about the to-and-fro it had taken me to get there.
Finally, in early July (day -101), my interview team went away to deliberate about me. I genuinely couldn’t tell which way it would go, and I’ve never in my life been so nervous to hear back about a job.
A large part of this is, of course, the high esteem in which I hold Automattic and the associated imposter syndrome I talked about previously, which had only been reinforced by the talented and knowledgable folks there I’d gotten to speak to during my trial. Another part was seeing their recruitment standards in action: having a shared space with other candidate developers meant that I could see other programmers who seemed, superficially, to be doing okay get eliminated from their trials – reality TV style! – as we went along. And finally, there was the fact that this remained one of my list of “dream companies”: if I didn’t cut it by this point in my career, would I ever?
It took 72 hours after the completion of my trial before I heard back.
I was to be recommended for hire.
It was late in the day, but not too late to pour myself a congratulatory Caol Ila.

Final Interview (day -94)
A lot of blog posts about getting recruited by Automattic talk about the final interview being with CEO Matt Mullenweg himself, which I’d always thought must be an unsustainable use of his time once you get into the multiple-hundreds of employees. It looks like I’m not the only one who thought this, because somewhere along the line the policy seems to have changed and my final interview was instead with a human wrangler (another super-friendly one!).
That was a slightly-disappointing twist, because I’ve been a stalker fanboy of Matt’s for almost 15 years… but I’ll probably get to meet him at some point or other now
anyway. Plus, this way seems way-more logical: despite Matt’s claims to the contrary, it’s hard to see Automattic as a “startup” any longer (by age alone: they’re two years
older than Twitter and a similar age to Facebook).
The final interview felt mostly procedural: How did I find the process? Am I willing to travel for work? What could have been done differently/better?
Conveniently, I’d been so enthralled by the exotic hiring process that I’d kept copious notes throughout the process, and – appreciating the potential value of honest, contemporaneous feedback – made a point of sharing them with the Human League (that’s genuinely what Automattic’s HR department are called, I kid you not) before the decision was announced as to whether or not I was to be hired… but as close as possible to it, so that it could not influence it. My thinking was this: this way, my report couldn’t help but be honest and unbiased by the result of the process. Running an unusual recruitment strategy like theirs, I figured, makes it harder to get honest and immediate feedback: you don’t get any body language cues from your candidates, for a start. I knew that if it were my company, I’d want to know how it was working not only from those I hired (who’d be biased in favour it it) and from those who were rejected (who’d be biased against it and less-likely to be willing to provide in-depth feedback in general).
I guess I wanted to “give back” to Automattic regardless of the result: I learned a lot about myself during the process and especially during the trial, and I was grateful for it!

One part of the final interview, though, was particularly challenging for me, even though my research had lead me to anticipate it. I’m talking about the big question that basically every US tech firm asks but only a minority of British ones do: what are your salary expectations?
As a Brit, that’s a fundamentally awkward question… I guess that we somehow integrated a feudalistic class system into a genetic code: we don’t expect our lords to pay us peasants, just to leave us with enough grain for the winter after the tithes are in and to protect us from the bandits from the next county over, right? Also: I’ve known for a long while that I’m chronically underpaid in my current role. The University of Oxford is a great employer in many ways but if you stay with them for any length of time then it has to be for love of their culture and their people, not for the money (indeed: it’s love of my work and colleagues that kept me there for the 8+ years I was!).

Were this an in-person interview, I’d have mumbled and shuffled my feet: you know, the British way. But luckily, Slack made it easy at least for me to instead awkwardly copy-paste some research I’d done on StackOverflow, without which, I wouldn’t have had a clue what I’m allegedly-worth! My human wrangler took my garbled nonsense away to do some internal research of her own and came back three hours later with an offer. Automattic’s offer was very fair to the extent that I was glad to have somewhere to sit down and process it before responding (shh… nobody tell them that I am more motivated by impact than money!): I hadn’t been emotionally prepared for the possibility that they might haggle upwards.
Three months on from writing my application, via the longest, most self-reflective, most intense, most interesting recruitment process I’ve ever experienced… I had a contract awaiting my signature. And I was sitting on the edge of the bath, trying to explain to my five year-old why I’d suddenly gone weak at the knees.

Getting Access (day -63)
A month later – a couple of weeks ago, and a month into my three-month notice period at the Bodleian – I started getting access to Auttomatic’s computer systems. The ramp-up to getting started seems to come in waves as each internal process kicks off, and this was the moment that I got the chance to introduce myself to my team-to-be.
I’d been spending occasional evenings reading bits of the Automattic Field Guide – sort-of a living staff handbook for Automatticians – and this was the moment when I discovered that a
lot of the links I’d previously been unable to follow had suddenly started working. You remember that bit in $yourFavouriteHackerMovie where suddenly the screen
flashes up “access granted”, probably in a green terminal font or else in the centre of a geometric shape and invariably accompanied by a computerised voice? It felt like that. I still
couldn’t see everything – crucially, I still couldn’t see the plans my new colleagues were making for a team meetup in South Africa and had to rely on Slack chats with my new
line manager to work out where in the world I’d be come November! – but I was getting there.
Getting Ready (day -51)
The Human League gave me a checklist of things to start doing before I started, like getting bank account details to the finance department. (Nobody’s been able to confirm nor denied this for me yet, but I’m willing to bet that, if programmers are Code Wranglers, devops are Systems Wranglers, and HR are Human Wranglers, then the finance team must refer to themselves as Money Wranglers, right?)
They also encouraged me to get set up on their email, expenses, and travel booking systems, and they gave me the password to put an order proposal in on their computer hardware ordering system. They also made sure I’d run through their Conflict of Interest checks, which I’d done early on because for various reasons I was in a more-complicated-than-most position. (Incidentally, I’ve checked and the legal team definitely don’t call themselves Law Wranglers, but that’s probably because lawyers understand that Words Have Power and must be used correctly, in their field!)

So that’s what I did this week, on day -51 of my employment with Automattic. I threw a couple of hours at setting up all the things I’d need set-up before day 0, nice and early.
I’m not saying that I’m counting down the days until I get to start working with this amazing, wildly-eccentric, offbeat, world-changing bunch… but I’m not not saying that, either.